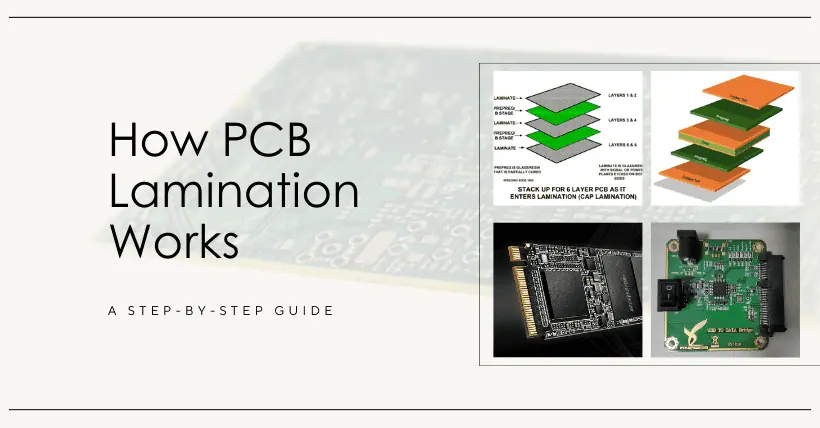
1. Principle of PCB Lamination
PCB lamination bonds and solidifies multi-layer materials under high temperature and pressure to form an integrated multi-layer board. The key material is the prepreg (PP film), which consists of epoxy resin and fiberglass. Under high temperature and pressure, the resin softens and flows, filling the gaps, forming a uniform bonding layer, and achieving a strong chemical bond through the diffusion and penetration of molecular chains.
| Structure Type | Content | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Structure | Isotactic polypropylene | The methyl groups are aligned consistently along the direction of the polymer main chain, forming a highly crystalline structure with high mechanical strength and thermal stability. |
| Syndiotactic polypropylene | The methyl groups are alternately arranged, the crystallinity is relatively low, and the performance is between isotactic and atactic. | |
| Atactic polypropylene | Methyl groups are randomly arranged, with an amorphous structure, usually exhibiting rubber-like properties, good flexibility but lower strength. | |
| Physical Structure | Crystalline area and non-crystalline area | PP film is composed of crystalline and non-crystalline regions. The crystalline region provides mechanical strength and thermal stability, while the non-crystalline region imparts flexibility. |
| Microstructure | Spherulites | The common microscopic structure in PP film, the size and distribution of spherulites affect its transparency and physical properties. |
| Processing Structure (such as BOPP) | Bilateral stretching | After biaxial stretching treatment, the PP film is stretched simultaneously in the machine direction and transverse direction, with the molecular chains oriented along the stretching direction, improving strength and transparency. |
2. PCB Lamination Process
The PCB lamination process mainly includes the following key steps:
✅ Material Preparation
- Core Board: Provides mechanical support and forms the basis of the multi-layer PCB.
- PP Material: Acts as the adhesive and is the key material for connecting the layers.
- Copper Foil: Used to form the outer circuit and needs to have good electrical conductivity and stability.
✅ Stacking and Positioning
- Stack the inner core board, PP material, and outer copper foil according to design requirements.
- Use thermal bonding or riveting methods for precise positioning to ensure alignment between the layers.
✅ Lamination and Heating
- Place the stacked materials into the lamination machine.
- Under high temperature and pressure, the resin in the PP softens and flows, filling the gaps between the core boards, ensuring tight bonding between the layers.
| Component Name | Function Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Plate | The upper and lower heating plates are used to provide uniform heat, allowing the semi-cured sheet to melt and bond tightly with the copper foil. |
| Pressure Device | Includes hydraulic cylinder, hydraulic pump, and pressure sensor, used to apply precise pressure to the upper mold. |
| Vacuum System | By using a vacuum pump to evacuate air between materials, it ensures that there are no bubbles during the lamination process. |
| Control System | Includes PLC controllers, human-machine interfaces, and sensors for precise control of temperature, pressure, and time. |
| Workbench | Fix the materials to be pressed to ensure their stability during the pressing process. |
| Cooling System | Used for quickly cooling materials after pressing is completed, ensuring the molding effect. |
✅ Cooling and Curing
- After lamination, cool the board to room temperature to cure the resin and form a stable multi-layer structure.
- The cooling process needs to be strictly controlled for temperature and pressure to avoid warping or delamination due to uneven cooling.
✅ Post-Processing
- Inspection: Perform size checks, circuit connection tests, and visual inspection.
- Trimming: Trim and polish the board to ensure the dimensions meet the design requirements.
3. Importance of Lamination Process
✅ Enhance Structural Strength and Stability
- The lamination process, by tightly bonding each layer under high temperature and pressure, enhances the mechanical strength and stability of the multi-layer board.
- It prevents warping and deformation, ensuring the reliability of the circuit board during subsequent assembly and use.
✅ Affect Electrical Performance and Impedance Characteristics
- The lamination process directly impacts the geometric structure and characteristic impedance of signal transmission lines.
- A well-designed lamination process ensures signal integrity and transmission quality, preventing signal attenuation and distortion.
✅ Concern for Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation
- The materials selected for the lamination process and the density after lamination affect the thermal conductivity of the PCB.
- A high-quality lamination process can provide better heat conductivity, ensuring efficient heat transfer from heat-generating components to the PCB surface.
Related:

Disclaimer:
- This channel does not make any representations or warranties regarding the availability, accuracy, timeliness, effectiveness, or completeness of any information posted. It hereby disclaims any liability or consequences arising from the use of the information.
- This channel is non-commercial and non-profit. The re-posted content does not signify endorsement of its views or responsibility for its authenticity. It does not intend to constitute any other guidance. This channel is not liable for any inaccuracies or errors in the re-posted or published information, directly or indirectly.
- Some data, materials, text, images, etc., used in this channel are sourced from the internet, and all reposts are duly credited to their sources. If you discover any work that infringes on your intellectual property rights or personal legal interests, please contact us, and we will promptly modify or remove it.