01
What is crystal orientation?
Simply put, crystal orientation refers to the “path” along which atoms are arranged in a specific direction inside a crystal. Crystal orientation is usually denoted by square brackets [hkl] to represent directions, round brackets (hkl) to represent planes, and angle brackets to represent families of directions.
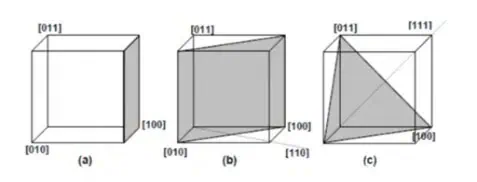
As shown in the figure below, [100] represents the direction along the x-axis of the lattice, [110] represents the diagonal direction (x+y), and [111] represents the space diagonal direction (x+y+z).
<100> is a family of directions, consisting of all equivalent [100]-type directions. <100> is perpendicular to the (100) crystal plane.
02
Why is crystal orientation so important?
Each orientation corresponds to different densities, atomic spacing, and bonding strengths. On a macroscopic level, the physical and chemical properties of a crystal vary significantly.
This is mainly reflected in:
- Defect density: Certain planes like (111) have relatively low surface defect densities.
- Surface smoothness: Surfaces like (100) tend to be flatter and smoother.
- Dopant solubility: Dopant atoms embed into the lattice differently depending on orientation.
- Etching rate: Wet and dry etching rates vary significantly across different planes.
- Epitaxial growth: The quality and rate of epitaxial growth depend on the crystal plane.
03
Applications of different crystal orientations:
<100>: Silicon wafers with this orientation account for the majority of total wafer production. Nearly all advanced CMOS logic chips are standardized on <100> silicon wafers. DRAM, SRAM, and flash memory also mainly use <100>-oriented silicon wafers.
<110>: These wafers make up only about 5% of wafer production. RF or power devices occasionally use silicon wafers with this orientation. MEMS processes frequently use <110>, <111>, or other custom orientations based on application.

Disclaimer:
- This channel does not make any representations or warranties regarding the availability, accuracy, timeliness, effectiveness, or completeness of any information posted. It hereby disclaims any liability or consequences arising from the use of the information.
- This channel is non-commercial and non-profit. The re-posted content does not signify endorsement of its views or responsibility for its authenticity. It does not intend to constitute any other guidance. This channel is not liable for any inaccuracies or errors in the re-posted or published information, directly or indirectly.
- Some data, materials, text, images, etc., used in this channel are sourced from the internet, and all reposts are duly credited to their sources. If you discover any work that infringes on your intellectual property rights or personal legal interests, please contact us, and we will promptly modify or remove it.


