In a world constantly evolving and advancing, China stands at the forefront of technological development. A significant aspect of this progress is the generation of nuclear energy to meet the country’s growing demands for electricity. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and in this case, it’s the management of nuclear waste. China generates a staggering 3,500 tons of nuclear waste annually, presenting unique challenges for the nation. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of nuclear waste, the methods employed to manage it, and the implications of this daunting task.
① Understanding Nuclear Waste
Nuclear waste is the byproduct of nuclear reactors’ operation, composed of various radioactive isotopes. These isotopes come in a wide range of characteristics, including long half-lives and the emission of high-energy particles and electrons. While the majority of these radioactive isotopes have relatively short half-lives, some pose significant challenges. Highly toxic radioactive isotopes like Krypton-81 and Lead-210 have half-lives ranging from thousands to tens of thousands of years, making their disposal a complex and long-term problem.
The Current State of Nuclear Waste Management
In China, the management of nuclear waste mainly involves intermediate-term storage and deep geological disposal. These methods aim to ensure the safe containment and eventual decay of radioactive isotopes. Let’s take a closer look at the steps involved in nuclear waste disposal:
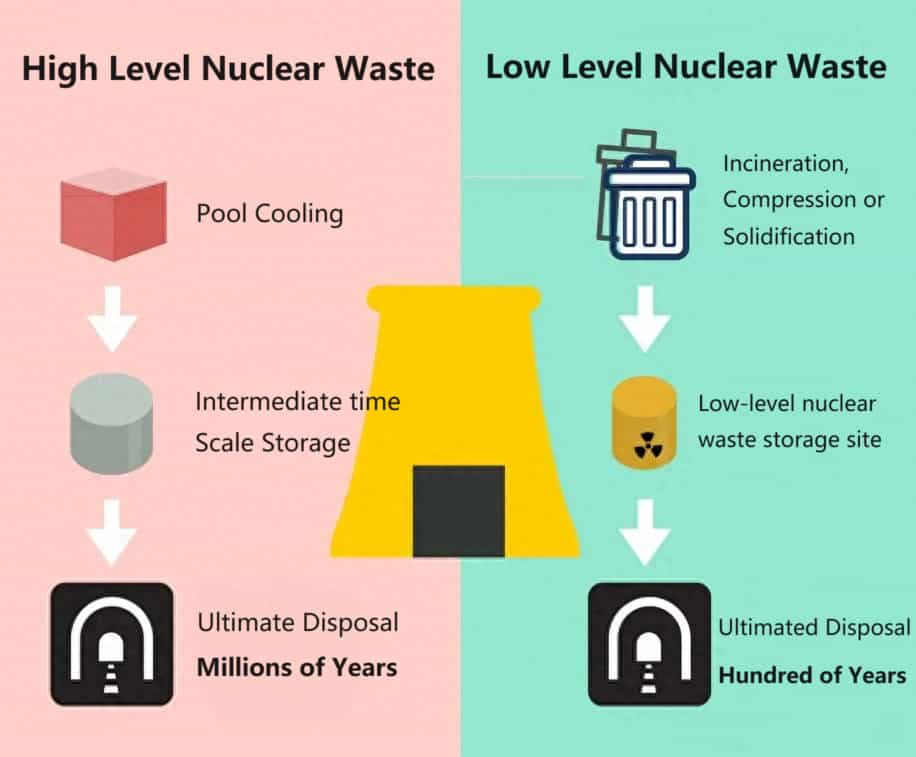
1. Solidification
The initial step in nuclear waste disposal is solidification. Radioactive waste is solidified with materials like cement or glass, ensuring it becomes stable and less likely to leak harmful radiation. This step is crucial in preparing the waste for transportation and burial.
2. Transportation
Once solidified, the nuclear waste is transported to remote deserts or wastelands, far away from densely populated areas. Transportation must be meticulously planned and executed to minimize the risk of accidents and radiation exposure.
3. Deep Underground Burial
After reaching the designated site, the waste is buried deep underground. This method, known as deep geological disposal, ensures that radioactive materials are contained, reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
4. Reduction of Nuclear Waste Volume
Another approach to nuclear waste management is the reduction of waste volume. This process involves separating and extracting useful elements from nuclear fuel, such as uranium, plutonium, iridium, and strontium. Once separated, the waste’s volume is reduced significantly, making it easier to manage. The resulting waste is then solidified and buried deep underground, just like the original waste.
The Challenges Ahead
Managing nuclear waste on such a massive scale is not without its challenges. The long half-lives of some radioactive isotopes mean that they will remain hazardous for thousands of years, necessitating secure containment. The logistical challenges of transportation and deep burial are immense, requiring a high level of precision and safety measures.
Furthermore, ensuring that these waste disposal methods remain safe and effective in the long run is a constant concern. With China’s energy demands continuing to rise, the amount of nuclear waste generated will only increase, putting more pressure on waste management infrastructure.
② Conclusion
China’s production of 3,500 tons of nuclear waste annually underscores the importance of effective and long-term nuclear waste management. The nation has put in place strategies such as solidification, transportation, and deep geological disposal to address this challenge. As technology and knowledge continue to evolve, we can hope for even more robust solutions in the future.
If you’re interested in further information on China’s nuclear energy or its waste management strategies, feel free to explore our FAQs below.
③ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is nuclear waste, and why is it a concern in China?
Nuclear waste is the byproduct of nuclear reactor operation, consisting of radioactive isotopes. In China, it’s a concern due to the large quantity generated and the long half-lives of some radioactive materials.
2. How does deep geological disposal work in nuclear waste management?
Deep geological disposal involves burying nuclear waste deep underground in carefully selected locations, ensuring long-term containment and safety.
3. Are there any innovative methods for nuclear waste management in China?
China is continuously exploring innovative methods, including advanced reprocessing technologies, to enhance nuclear waste management.
4. What are the risks associated with transporting nuclear waste to remote locations?
The risks include accidents during transportation, potential radiation exposure, and ensuring the safety of local communities along the transportation route.
5. What’s the outlook for nuclear waste management in China given its growing energy needs?
Nuclear waste management will remain a significant concern as China’s energy needs grow. Continued research and development are essential to finding more efficient and sustainable solutions.
Related:

Disclaimer: YUNZE maintains a neutral stance on all original and reposted articles, and the views expressed therein. The articles shared are solely intended for reader learning and exchange. Copyright for articles, images, and other content remains with the original authors. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.



