Despite being available for over two years, DDR5 memory, due to DDR4’s compatibility and cost-effectiveness, remains the mainstream choice in the market. Initially, DDR5 memory and compatible motherboards were expensive. Now that DDR5 memory is becoming more affordable, many considering new builds wonder: Should they go for DDR4 or DDR5 (Unveiling DDR5) memory? Especially for gamers, is there a significant difference between DDR4 and DDR5 memory in gaming performance? Below, we discuss the differences and offer purchasing advice.
Let’s first understand the differences between DDR4 and DDR5 memory.
Differences between DDR4 and DDR5 memory #
a. Memory Frequency #
Memory Frequency The most noticeable difference between DDR4 and DDR5 memory is their frequency. DDR5 achieves double the frequency compared to DDR4. While DDR4 initially had frequencies of 2133 and 2400MHz, mainstream frequencies now reach 3200MHz and 3600MHz. Flagship DDR4 memory can even go up to 4266MHz or higher. On the other hand, DDR5 memory starts at 4800MHz and commonly ranges from 5200MHz to 6000MHz, with flagship versions reaching 8000MHz.
b. Memory Bandwidth #
Memory Bandwidth DDR5 offers faster data transfer rates, resulting in higher memory bandwidth. For example, at DDR4’s 3200 frequency, the bandwidth is 25.6GBps, while DDR5’s 4800 frequency provides 38.4GBps bandwidth.
c. Operating Voltage #
Operating Voltage DDR5 boasts better energy efficiency than DDR4. DDR4 operates at 1.2V, whereas DDR5 operates at a lower voltage of 1.1V, reducing power consumption by 8% and offering enhanced power-saving benefits.
d. PMIC Power Management Chip #
PMIC Power Management Chip Unlike DDR4, where the PMIC power management chip is integrated into the motherboard, DDR5 integrates the PMIC power management chip onto the memory’s PCB. It acts as the brain of an intelligent voltage regulation system, monitoring current while promoting voltage ramps and configurable voltage levels. This eases the burden on the motherboard’s power management.
e. Single-Chip Density #
Single-Chip Density DDR5 achieves higher single-chip density, with individual chips reaching capacities of 16GB. In contrast, DDR4 single chips only have a capacity of 4GB. Consequently, DDR5 memory modules can offer larger overall capacities, with a single module potentially reaching 128GB or even 256 GB. However, current consumer-level demands do not typically require such large memory capacities.
f. ECC Memory Error Correction Mechanism #
DDR5 memory introduces an ECC error correction feature, but it’s different from traditional ECC. In DDR5, an On-die ECC error correction function is added. This can be seen as a budget version of ECC, as On-die ECC only corrects errors within the memory module itself. Traditional ECC often involves extra chips dedicated to error correction, capable of rectifying communication errors during operation.
The ECC function in DDR5 primarily enhances memory stability and reduces the likelihood of blue screens.
g. Single-Module Dual-Channel #
Normally, dual-channel requires two DDR4 modules, but a single DDR5 module can achieve a form of dual-channel, though not a true one; it’s more like a pseudo-dual channel.
Think of it this way: DDR4 memory originally had a single 64-bit channel for data transmission, while dual-channel is 2x 64 bits. DDR5 memory splits the channel into two 32-bit channels, achieving a single-module dual-channel effect. To achieve the ideal values of true dual-channel, two modules are still needed to form a dual-channel configuration.
h. XMP 3.0 Technology #
XMP 3.0 is Intel’s one-click overclocking technology for DDR5 memory. It stores optimized preset parameters. Compared to XMP 2.0, XMP 3.0 offers five profiles, including three fixed configurations and two user-customizable ones. Profile names are customizable, and the module voltage is adjustable. Some manufacturers have introduced user-friendly overclocking software, lowering the barriers to overclocking.
i. Interface Differences #
DDR4 and DDR5 have slightly different notches, meaning they are not cross-compatible. If you want to use DDR5 memory, your motherboard must have DDR5 slots to be compatible with DDR5 memory. DDR5 memory cannot be used in DDR4 slots.
j. Timings #
Timings are a challenge with DDR5 memory. Due to the drastic increase in DDR5 memory frequency, while lowering power consumption, higher timings are necessary for stability. For example, a DDR4 2666 frequency memory typically has timings between CL17 and CL19, while a DDR5 4800 frequency memory commonly has timings around CL40. Higher memory timings result in higher latencies. Therefore, DDR4 memory might have an advantage in games that are more sensitive to memory latency.
Let’s take a look at the gaming performance between DDR4 and DDR5 memory. Are there significant differences? Let’s examine the data.
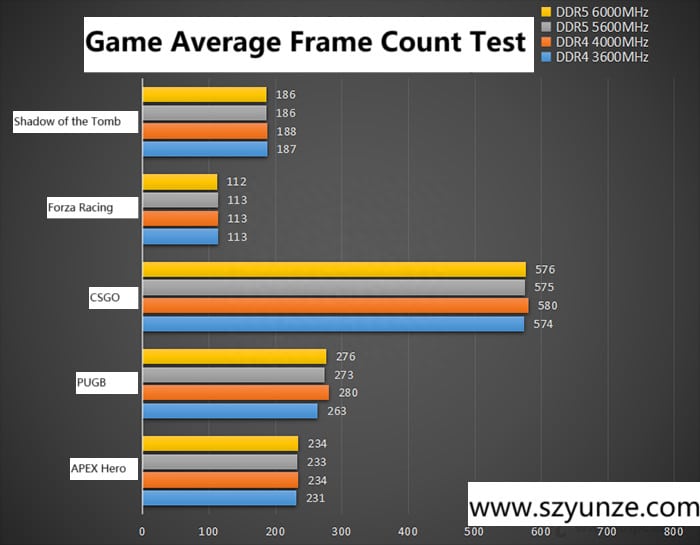
At a 2K resolution, running tests on games with the highest graphics settings, we observe that the gaming performance difference between DDR4 and DDR5 is not substantial. They both have their strengths and weaknesses, and the frame rates between the two are not significantly different.
Tips for Choosing Between DDR4 and DDR5 Memory #
While DDR5 memory boasts higher frequencies and bandwidth, the elevated latencies often negate substantial gaming improvements. For gamers seeking a good value, DDR4 memory can still be a viable option, given the more affordable pricing of motherboards and memory modules. However, for those with productivity needs, choosing DDR5 memory is advisable due to its significant bandwidth advantage, which can greatly benefit productivity tasks. When it comes to DDR5 memory, it’s not recommended to opt for 4800MHz, as its performance is subpar. Personal recommendation starts at 5600MHz, ideally 6000MHz or higher.
Related Reading:






