In the ever-evolving landscape of data storage solutions, solid-state drives (SSDs) have emerged as a game-changing innovation, promising faster data access speeds, enhanced durability, and efficient power consumption. To truly harness the capabilities of SSDs, it’s crucial to delve into the intricacies of their architecture and functionality. In this comprehensive guide, we, as experts in the field, will unravel the concept of over-provisioning in SSD technology and its profound impact on SSD performance and longevity.
What is Over-Provisioning? #
Over-provisioning, often referred to as “OP,” is a strategic allocation of extra NAND flash memory capacity beyond what is publicly advertised in an SSD’s specifications. This surplus space is not visible to the user but plays a pivotal role in enhancing the drive’s overall performance and reliability.
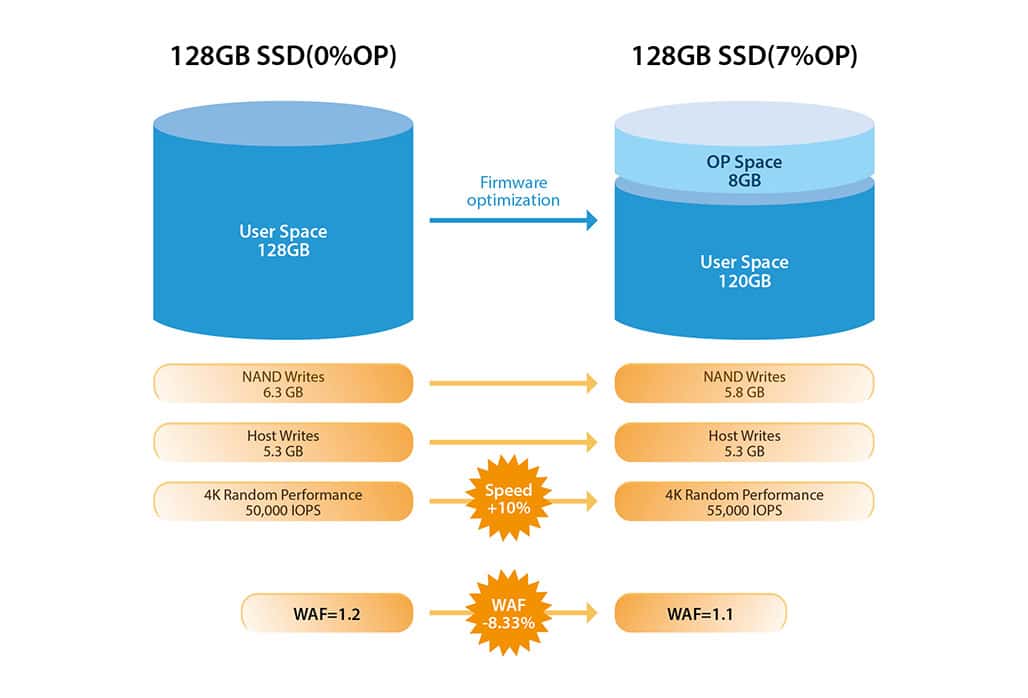
The Benefits of Over-Provisioning #
1. Improved Write Performance #
One of the most significant advantages of over-provisioning is its direct impact on write performance. By allocating additional NAND flash memory for buffering, an SSD can efficiently manage write requests. This prevents write amplification, a phenomenon where data is rewritten multiple times, ultimately decreasing the wear and tear on the drive and ensuring consistent write speeds.
2. Enhanced Longevity #
Over-provisioning also contributes to the extended lifespan of SSDs. With more reserved space to distribute write and erase cycles, each memory cell is subjected to fewer program/erase operations, reducing cell wear and extending the drive’s overall lifespan. This makes over-provisioned SSDs an excellent choice for tasks with high write loads, such as servers and workstations.
3. Improved Read Performance #
While over-provisioning primarily addresses write-related concerns, it indirectly benefits read performance as well. The reduced write amplification not only extends the SSD’s life but also ensures that the drive maintains consistent read speeds over time, making it suitable for various applications.
Why Use Over-Provisioning #
OP has a direct effect on SSD performance under sustained workloads and as the drive is filled with data. Guaranteeing free space to accomplish the NAND management tasks discussed above (Garbage Collection, Wear-Levelling, Bad Block Management) means the SSD (Which Users need to reserve Over-Provisioning?) does not have to waste time preparing space on demand, a process that requires additional time as data is copied, erased, and recopied. An added benefit is that OP makes all of the SSD maintenance procedures more efficient, reducing the WAF by ensuring there’s room to work.
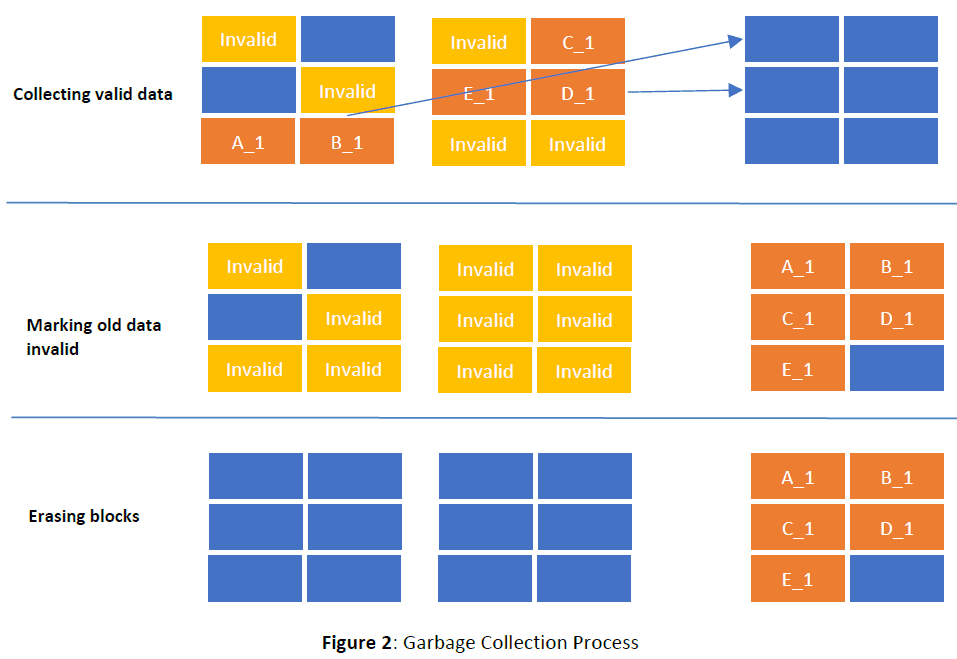
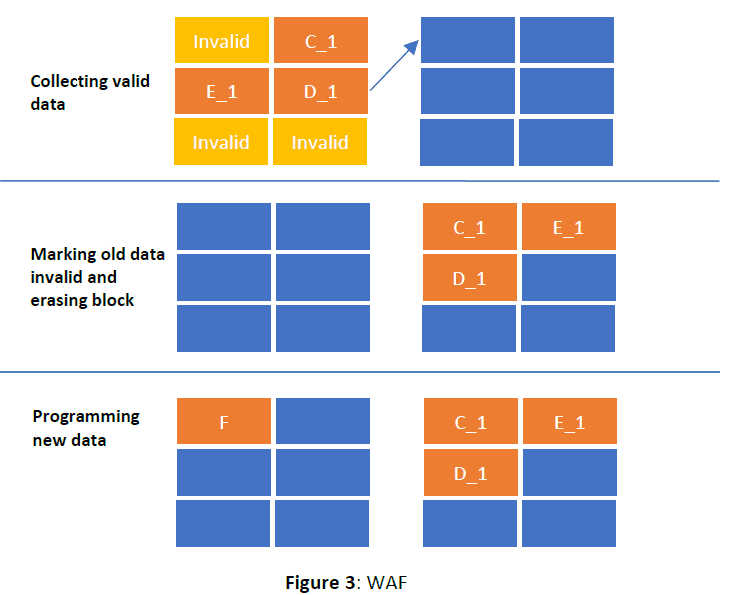
Consider this scenario: You are a chef with very limited counter space (say one arm’s length across and half an arm’s length deep). Preparing a 5-course meal in such a limited area would mean you have to waste a lot of time moving things around or putting them away to make room for other tasks. Now, imagine you quadruple your workspace. You can leave everything you need at hand, reduce repeating steps (like getting the salt from the pantry and putting it back away), and increase your working speed. The same goes for SSDs. Give them more room to work, and they can do it more quickly and efficiently, reducing WAF and increasing performance at the same time.
Types of Over-Provisioning #
1. Factory Over-Provisioning #
Some SSD manufacturers opt for factory over-provisioning, where a portion of the NAND flash memory is permanently reserved for OP. This type of OP is not user-configurable and is established during manufacturing. It is crucial to check the specifications provided by the manufacturer to understand the extent of factory over-provisioning in your SSD.
2. User-configurable over-provisioning #
User-configurable over-provisioning allows users to manually allocate a portion of the SSD’s free space for OP. This gives you more control over the balance between performance and capacity, making it an attractive option for those with specific usage requirements.
Implementing Over-Provisioning #
To implement over-provisioning, follow these steps:
- Check Your SSD: Determine if your SSD already has factory over-provisioning. If not, proceed to the next step.
- Backup Data: Before making any changes, ensure you have a backup of your data to prevent data loss.
- Use SSD Management Software: Many SSD management tools allow you to allocate free space for over-provisioning. Consult your SSD manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended software.
- Allocate Space: Configure the desired amount of free space for over-provisioning. A common recommendation is 7-10% of the drive’s total capacity.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor your SSD’s performance to ensure that over-provisioning continues to provide the desired benefits.
Conclusion #
In the realm of SSD technology, over-provisioning stands as a crucial strategy to maximize performance, increase longevity, and maintain consistent read and write speeds. Whether your SSD comes with factory over-provisioning or allows user-configurable options, understanding and leveraging over-provisioning will undoubtedly elevate your storage experience. Invest in over-provisioned SSDs for a seamless and reliable computing experience.
Recommended Reading:






