
By the end of 2019, the Tesla Cybertruck was undoubtedly stealing the limelight. Its appearance alone set it apart from many other pickup truck series. I believe that the first thought that came to most people’s minds when they saw the car was: ugly! But after looking at it more closely, they would sincerely say: it’s really ugly!
You guys actually said it’s ugly? Elon Musk was quite dissatisfied. Although your aesthetics haven’t reached my level yet, this car is very durable. So, he asked Tesla’s Chief Designer, Franz von Holzhausen, to demonstrate the strength of the pickup’s glass. He threw a round metal ball at the driver’s side window, and surprisingly, the glass shattered.
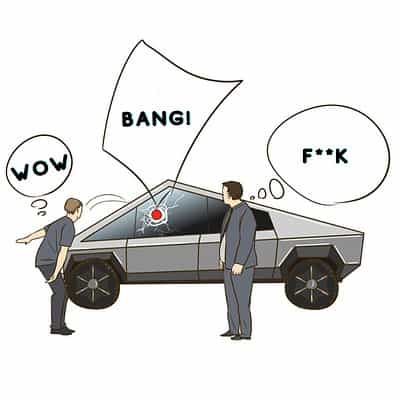

Despite the glass not completely shattering, the scene was quite awkward. To lighten the mood, Musk joked, “Perhaps you threw it too hard.” Then, the Chief Designer picked up the metal ball again and smashed it against the rear passenger window, and the glass shattered once more.
Shattered again…
Shattered…
Shattered.
However, humans can never escape the law of “true fragrance.” After just one week of open reservations, the Cybertruck received 250,000 orders.
Whether it’s considered “fragrant” or not, this is the coolest pickup truck ever released. Elon Musk, who is usually immersed in the role of the overlord and can’t help himself, personally drove it out to show off its coolness.
One mountain cannot contain ‘Three M’
Many people mistakenly believe that Elon Musk is the founder of Tesla, but the truth is that Musk joined later, and the actual founders were two “M“s – American genius engineers Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning.
The reason why the two of them decided to start a company together was simple: they wanted to create those cool electric cars that were not available in the market. Since they couldn’t buy one, they had to build it themselves.
The name “Tesla” comes from the great inventor Nikola Tesla and was proposed by Martin and his wife during a trip to Disneyland in January 2003.
On July 1, 2003, with high hopes of building high-performance electric sports cars, the two “M“s formed Tesla in Delaware. Finally, after one year and eight months after the company’s founding, in 2004, Tesla reported a net loss of $2.4 million for the year. Looking back to the time after Tesla’s establishment, Martin and Marc felt like they had cut a piece of cake that was too big to digest. Tesla was rapidly burning through money during its investment in research and development and production at a visible pace.
As the company was on the brink of running out of funds, and the two “M“s were at a loss, a third “M” came into the picture – Elon Musk.

In April 2004, Tesla secured a Series A funding round of $7.5 million, with $6.35 million coming from Elon Musk. Already keen on the electric vehicle industry, Musk laid out his conditions for the investment: he would take control of Tesla, become the Chairman of the company, and have the ultimate decision-making authority on all matters.
Subsequently, conflicts arose among the three “M”s. “Magnate M” Musk continued to invest heavily, while the two “M”s, Martin and Marc, were ousted from the board of directors. From that point on, Tesla was solely driven and dominated by Musk, grabbing all the attention and leading the way.
Why do outstanding people tend to drop out of school?
Elon Musk, born in 1971 in South Africa, immigrated to the United States at the age of 18. In 1992, he received a scholarship to attend the University of Pennsylvania, where he earned degrees in economics and physics.
Before officially starting his entrepreneurial journey, Musk initially intended to pursue further studies at Stanford University. However, he was quickly tempted by the wave of the internet and dropped out after just two days of classes to embark on his entrepreneurial ventures.

After dropping out of school, Musk co-founded Zip2 with his partners. In 1999, they sold Zip2 to Compaq for $340 million.
In 1999, Musk founded X.com (the predecessor of PayPal), which became the world’s largest online payment platform. In 2002, he sold it to eBay for $1.5 billion.
In 2002, Musk created SpaceX, where he serves as the CEO. SpaceX is a rocket and spacecraft manufacturer, providing space supply services to NASA and satellite launch services to companies like Iridium. It became the first privately-funded company to send a rocket into space.
In 2004, Musk invested $6.3 million to take control of Tesla, while the founder Martin Eberhard became the CEO.
In 2006, Musk co-founded SolarCity, a publicly traded company specializing in distributed solar energy generation.
Why does Tesla, a company that has been continuously burning through money, seem to never run out of it?
Tesla incurred a net loss of $2.4 million in its first year, 2004.
In the second year, 2005, the net loss increased to $11.6 million.
By the third year, 2006, Tesla launched its first mass-produced car, the Roadster, selling 127 units within two weeks. However, the net loss for that year reached $30 million.
In the fourth year, 2007, Tesla’s preorders for the Roadster exceeded 400 units, but the net loss for the entire year was $78 million.
Fast forward to 2013, the company’s 10th year, Tesla achieved a fourfold increase in revenue, and the net loss was reduced by 80% to $74.014 million compared to $396.213 million in 2012.
Despite burning through money each year, how does Tesla manage to keep going and remain resilient?
Financing Refinancing, the founders dig deep into their pockets

On February 1, 2005, Tesla completed its second round of financing led by Musk, raising a total of $13 million in Series B funding. In July of the same year, Tesla signed a production contract with Lotus Cars for the manufacturing of the Roadster.
On May 31, 2006, Tesla announced that it had completed a Series C funding round, raising $40 million. The round was led by VantagePoint Venture Partners and Musk. Other institutional investors included Draper Fisher Jurvetson and JP Morgan Bay Area Equity Fund. Notably, individual investors like Larry Page and Sergey Brin, the co-founders of Google, and Nick Pritzker also participated in the investment.

The development of the Roadster took three years, and the initial projected development cost of $25 million had already depleted $140 million by 2008. To raise funds, Musk even had to sell his own sports car and personal assets.
On February 19, 2008, Tesla issued convertible bonds, raising $55 million in Series E funding. This marked the completion of their fifth round of financing.
In June 2010, Tesla went public on the NASDAQ stock exchange, becoming the second American car company to be listed after Ford in 1956.
On May 2, 2019, Tesla announced its plan to raise funds from the capital market by issuing 2.72 million new shares and $1.35 billion in convertible bonds. The company aimed to raise $650 million through the new stock issuance, and Musk expressed his intention to buy back up to $10 million worth of shares.
Since taking over Tesla, Musk has continuously invested a substantial amount of his own wealth into the development of the company.
Additionally, his personal charisma and dedication to technology research and development have attracted other prominent figures to also invest in Tesla. The future development of Tesla is now closely linked to Musk’s personal wealth.
The Field of Electric Vehicles is Unrivaled
In the second quarter of 2019, Tesla captured a quarter of the luxury car market in the United States and secured a 14% market share in the European electric car market.
In the third quarter of 2019, Tesla reported its best-ever financial results, with the stock price surging over 20% after-hours, reaching its highest value since February, and crossing the $300 mark again. The company finally achieved net profitability.
Currently, Tesla dominates the electric vehicle industry and has no substantial competitors. Neither the “Taycan” from Porsche nor Audi’s “e-tron” poses a significant threat to Tesla’s Model S and Model 3.
Charging infrastructure is a crucial issue for electric vehicles.
Tesla has already established its global charging network with 1,604 Supercharger stations and 14,081 Supercharger stalls worldwide as of 2019. In just two years, this number has nearly doubled from around 800 stations and over 5,000 stalls in 2017. In China, Tesla’s charging network covers more than 130 cities, with over 1,700 Supercharger stalls and over 2,100 Destination Charger stations.
Recommended Reading:
- How Tesla and NIO Thrive with Minimal SKUs?
- SSD 4K Random Read Slower Than Write: Simple Explanation

1. This article is compiled from online sources. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.
2. The published content represents the views of the author and not the position of Yunze.


